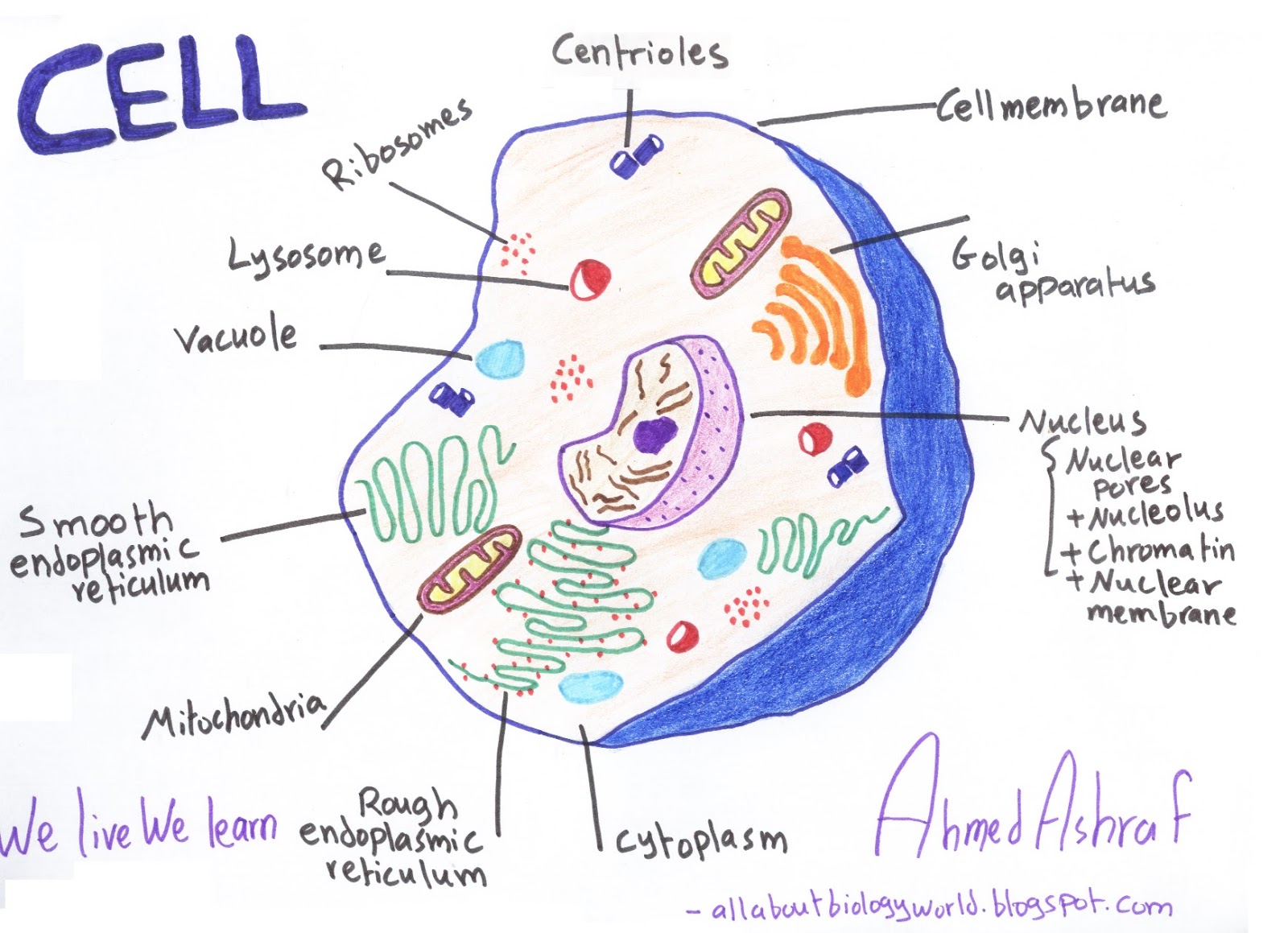
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder
Eukaryotic cells are much more complicated than those of prokaryotes. They are packed with a fascinating array of subcellular structures that play important roles in energy balance, metabolism, and gene expression.
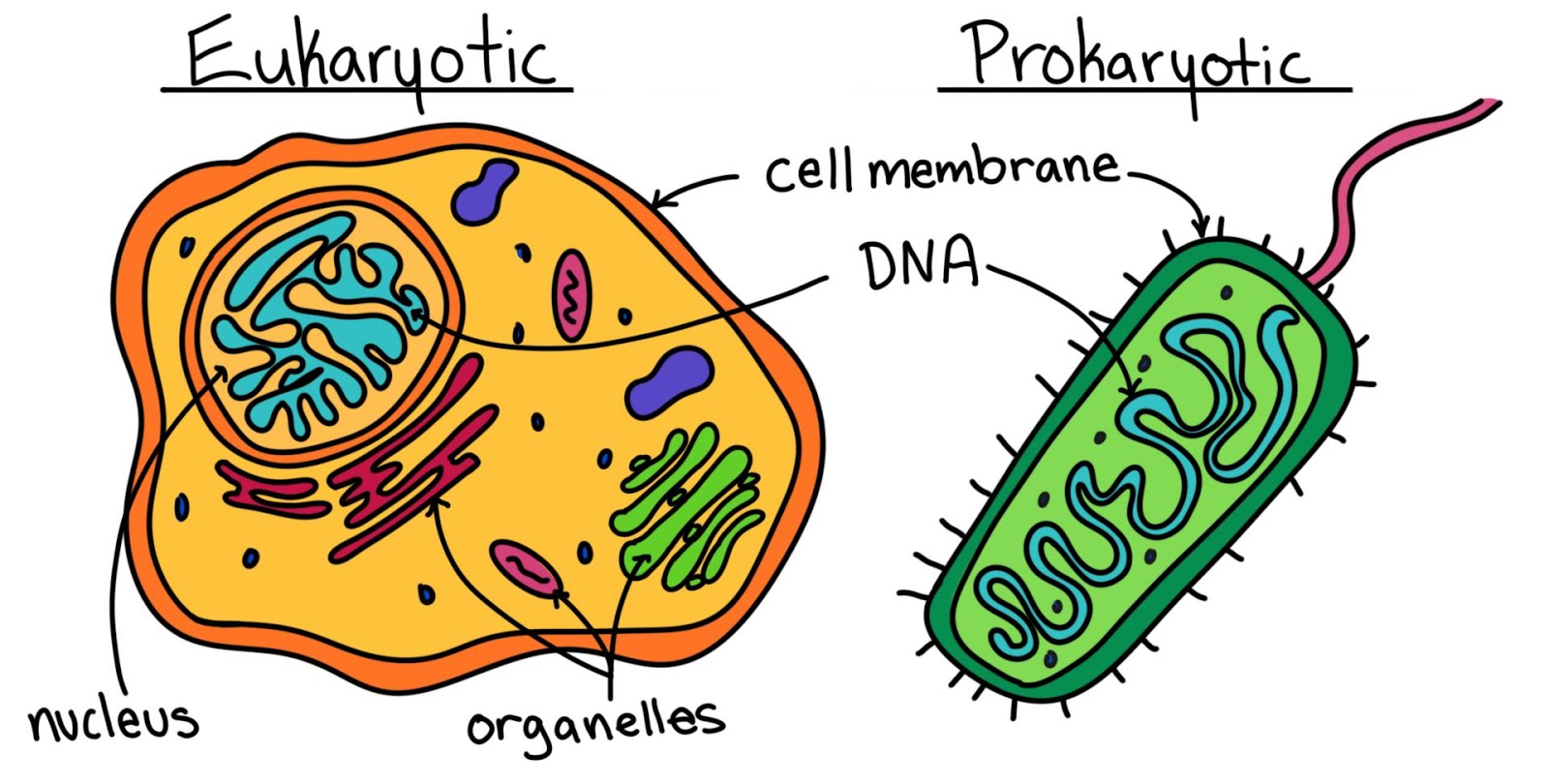
Bilingual Year 6 What are the different type of cells?
Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the structure of eukaryotic plant and animal cells State the role of the plasma membrane Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles Describe the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix

1.4. Eucaryotic cell structure Biolulia European Sections
Eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Figure 2.3.1 - Annotated drawing of an animal cell 2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure.

Eukaryotic Cells The Cell MCAT Biology Review
The Plasma Membrane. Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane ( Figure 3.8) made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone, and a phosphate group.

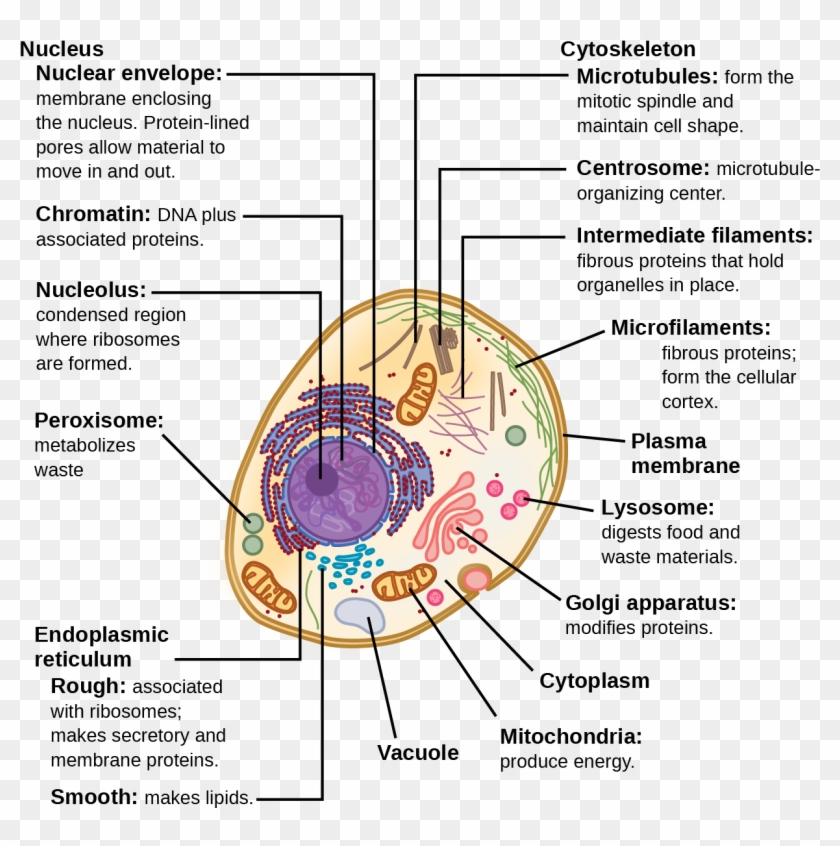
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures. Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting. Plasma Membrane: All cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, have a plasma membrane.
Chromatin Drawing Eukaryotic Cell Structure Of A Typical Eukaryotic
Characteristics Structure Diagram Cell Cycle Examples What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.

the structure of a plant cell labeled in black and white, with labels
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus."

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.

Eukaryote cell vector simple Stock vector Colourbox
The Cell Wall. In Figure 3.3. 1 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. Fungal and protist cells also have cell walls.
2.3 Eukaryotic cell BIOLOGY4IBDP
26K views 8 years ago Topic 1: Cell Biology (Old Syllabus Last Exams 2024) Drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Also identifying the difference.
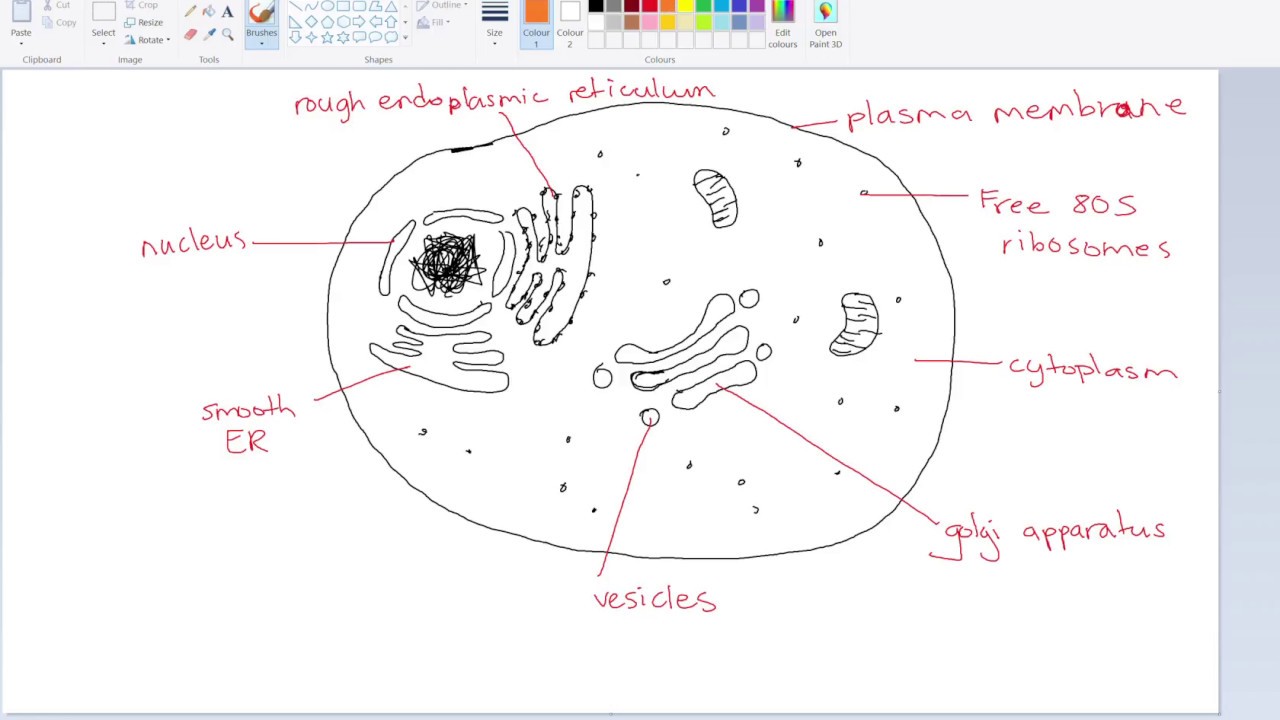
How to draw a Eukaryotic Cell IB Biology YouTube
How to draw Eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginners eukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram, diagrams, how to.
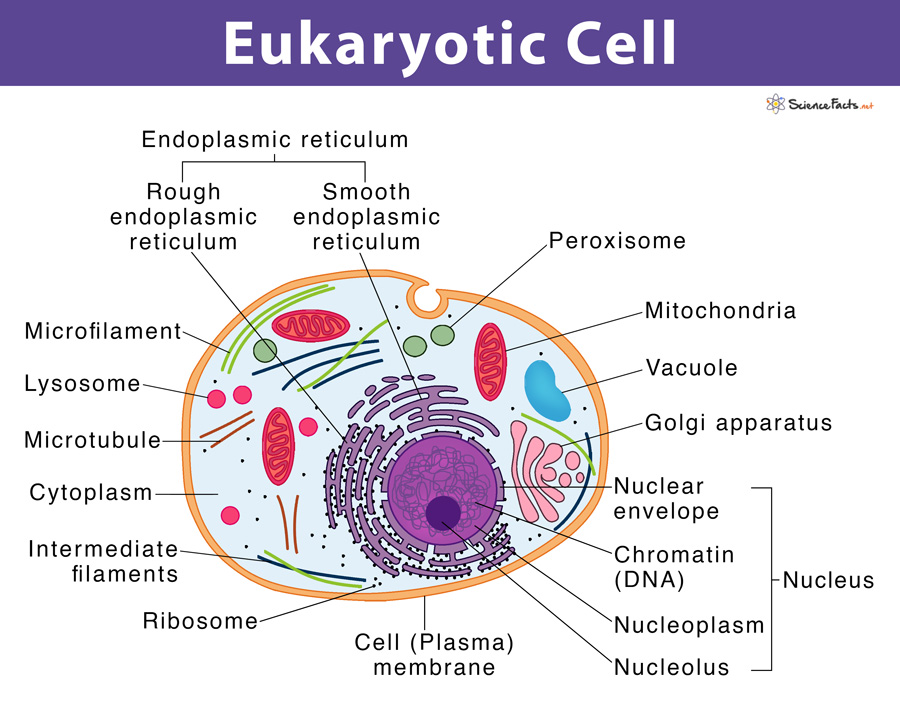
Eukaryotic Cells Definition Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Parts Structure
Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. Eukaryotic cells also have organelles, which are membrane-bound structures found within the cell.

identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell
Introduction to eukaryotic cells. By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others.
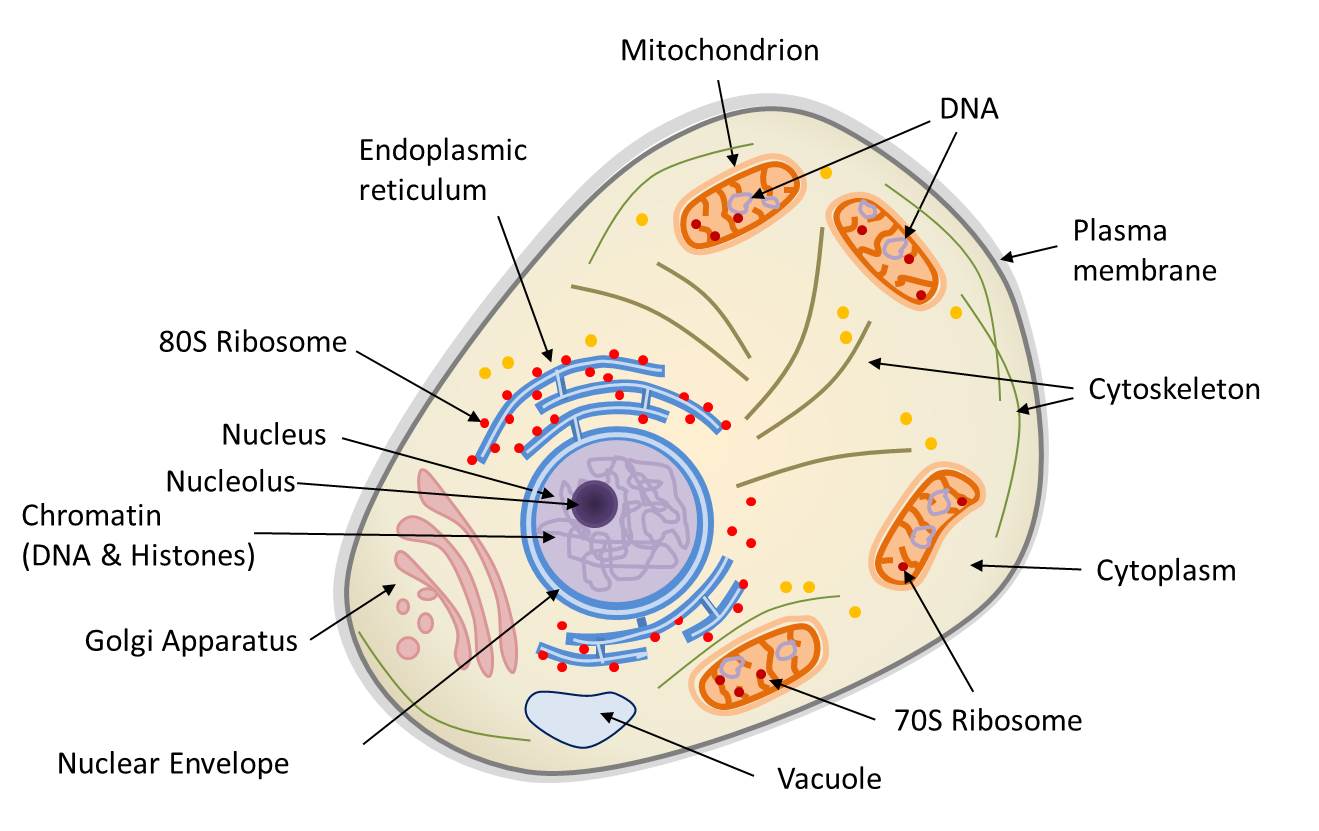
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.

Eukaryotic Cell Drawing Simple
A. The Nucleus. The nucleus separates the genetic blueprint, i.e., DNA from the cell cytoplasm. Although the eukaryotic nucleus breaks down during mitosis and meiosis as chromosomes form and cells divide, it spends most of its time in interphase, the time between cell divisions.This is where the status of genes (and therefore of the proteins produced in the cell) is regulated.
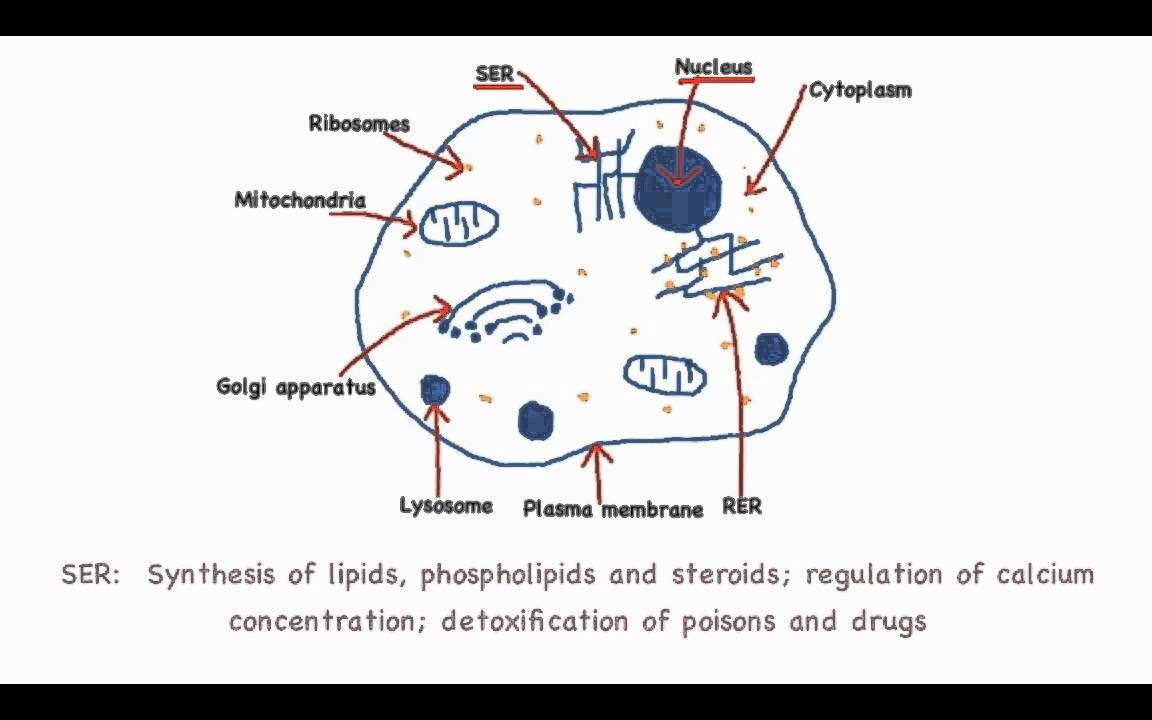
1.2 Skill Drawing eukaryotic cells YouTube
Join this channel to get access to perks:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCVHs8_j7936v-Vh2fqKRcjQ/join#Eukaryoticcelldiagram #Eukaryoticcelldrawing #Eukaryot.